Creating Custom ASP.NET Middleware: A Step-by-Step Guide
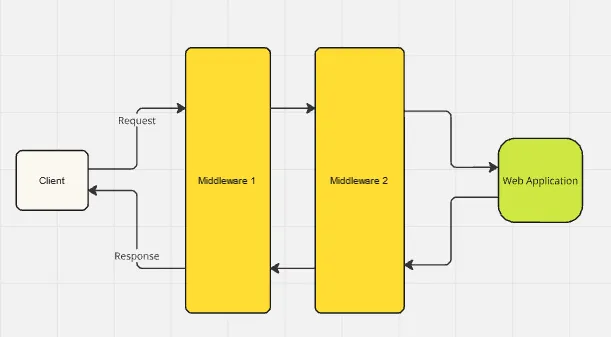
Middleware in ASP.NET Core acts as a pipeline through which every HTTP request passes before reaching your application’s core logic. Think of it as a series of gates or filters that process incoming requests and outgoing responses.
Where Does Middleware Fit?
Middleware can modify requests, verify conditions, log data, or handle exceptions before they reach the main application logic. This flexibility allows for efficient and centralized processing but also requires careful consideration of performance impacts.
Example: Timing Requests with Custom Middleware
Here’s a simple example of custom middleware that measures the time taken for a request to process:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
public class CustomMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
public CustomMiddleware(RequestDelegate next)
{
_next = next;
}
public async Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context)
{
// Start timing
var stopwatch = new Stopwatch();
stopwatch.Start();
await _next(context); // Pass request to next middleware/controller
// Stop timing and log the elapsed time
stopwatch.Stop();
var elapsedTime = stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds;
Console.WriteLine($"Request took {elapsedTime} ms");
}
}
In this example, the middleware logs how long each request takes by timing the execution before and after it’s processed by the application’s controller.
Integrating Middleware into Your Application
To use this middleware, add it to the pipeline in the Startup class:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
public class Startup
{
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
// Register your custom middleware
app.UseMiddleware<CustomMiddleware>();
// Additional middleware can be added here
}
}
Middleware can be stacked, allowing for multiple pieces to be executed in sequence. Keep in mind that each piece adds to the processing time of every request, so it’s important to balance functionality with performance.
Final Thoughts
This example demonstrates the basics of custom middleware. From here, you can expand the functionality to suit various needs, such as authentication, error handling, or data logging. Remember, effective middleware can greatly enhance your application, but always be mindful of performance implications.
Read in Thai: Click here